Planar magnetic headphones have been the tip of the spear during the Head-Fi revolution and you are more likely to find consumers who have heard of the technology because of the exponential growth of the high-end headphone market versus those who have experienced planar or ribbon loudspeakers.
Edward W. Kellogg and Chester W. Rice are credited with inventing the first ribbon loudspeaker while they were working at General Electric in 1924. They discovered that a thin metal ribbon suspended in a magnetic field could be used to produce sound waves, and this design has been refined and improved upon over the decades.
Dr. Oskar Heil was also a pioneer when it comes to ribbon loudspeakers in the 1930s. Heil was a German physicist and inventor who was interested in developing new types of loudspeakers that could produce high-quality sound across a wide frequency range. Heil’s design used a thin strip of metal foil suspended in a magnetic field to produce sound.
The ribbon loudspeaker was initially used in military and industrial applications, but it later became popular in high-end audio systems due to its ability to reproduce sound with exceptional clarity and detail.
Audiophiles have enjoyed the benefits of planar/ribbon loudspeakers for almost 50 years, and many of us have owned loudspeakers created by Magnepan, Eminent Technology, Infinity, and Apogee Acoustics. New brands like Diptyque and Clarisys Audio are offering new ribbon designs that offer even more impressive performance.
Ribbon tweeters have become extremely common and one can find them in loudspeakers manufactured by Quad, MartinLogan, Adam Audio, Emotiva, Aperion, and Monoprice.
Like other planar loudspeakers (electrostatic), planar magnetic loudspeakers use a flat diaphragm to produce sound. However, instead of using an electrostatic charge to move the diaphragm, planar magnetic drivers use a magnetic field.
The diaphragm is suspended between two rows of magnets, and when an electrical signal is applied to the voice coil, it interacts with the magnetic field to move the diaphragm and produce sound.
The diaphragm is usually made of a thin film or foil material, such as Mylar or Kapton, and is mounted between two sets of magnets, one on either side of the diaphragm.

When an electrical signal is applied to the conductive trace pattern, a magnetic field is created that interacts with the magnets and causes the diaphragm to move, producing sound waves. The movement of the diaphragm is much more precise and controlled than in traditional cone drivers, which can lead to improved clarity and detail in the sound.
Planar magnetic loudspeakers are known for their ability to produce very accurate, detailed sound with low distortion.
Ribbon and planar magnetic loudspeakers also features a dipole radiation pattern, which means that the sound is radiated equally from both the front and the back of the speakers. This results in a more spacious and natural soundstage, as the sound is not confined to a single direction.
However, they can be more expensive to manufacture than traditional cone drivers, and they may require more power to drive than other types of loudspeakers. Additionally, planar magnetic loudspeakers can be quite large and heavy, which can make them difficult to install in some environments.

Advantages?
Planar magnetic loudspeakers offer several advantages over other types of loudspeakers:
- Accuracy and Detail: Planar magnetic drivers are known for their ability to produce accurate, detailed sound with low distortion. They can reveal subtle nuances in music and reproduce complex sounds with clarity.
- Wide Frequency Response: Planar magnetic drivers have a wider frequency response than traditional cone drivers, meaning they can reproduce a broader range of frequencies with more accuracy.
- Low Distortion: Planar magnetic drivers have lower distortion than traditional cone drivers, which means that they can produce sound with greater clarity and accuracy.
- Speed and Responsiveness: Planar magnetic drivers have a faster response time than traditional cone drivers, which allows them to reproduce transient sounds with greater accuracy and speed.
- Durability: Planar magnetic drivers can be more durable than traditional cone drivers, as they have fewer moving parts that can wear out over time. However, that “durability” also comes with the understanding that planar and ribbon drivers are also fragile and can be damaged rather easily.
Disadvantages?
While planar magnetic loudspeakers offer several advantages, they also have some disadvantages to consider, including:
- Cost: Planar magnetic drivers are generally more expensive to manufacture than traditional cone drivers. This can make them cost-prohibitive for some consumers.
- Size and weight: Planar magnetic loudspeakers are often larger and heavier than traditional cone drivers. This can make them difficult to move around or fit into smaller spaces.
- Amplifier requirements: Planar magnetic drivers have a low impedance and require a powerful amplifier to drive them properly. This can add to the overall cost of a system.
- Limited bass response: Planar magnetic drivers can struggle to reproduce very low frequencies due to the large size of the diaphragm needed to move enough air. This means that a separate subwoofer may be necessary to achieve good bass performance.
Overall, planar magnetic loudspeakers are a specialized type of loudspeaker that can offer superior sound quality in certain applications, but they may not be the best choice for every listener or environment.
It’s important to consider the specific needs and requirements of your audio system when deciding whether to invest in planar magnetic loudspeakers.
Here is a list of some ribbon/planar loudspeakers or models that utilize a ribbon driver technology.
- Magnepan 30.7 – A high-end, full-range ribbon loudspeaker that features a 4-ohm impedance and a frequency response range of 20Hz to 40kHz.
- Piega Master Line Source 2 Gen2 (top photo above) – This 3-way dipole system with acoustic lens technology uses a line source array of ribbon drivers for mid and high frequencies.
- Raidho X1.6 – A two-way loudspeaker that features a custom ribbon tweeter and a 6.5-inch bass driver.
- Apogee Acoustics Scintilla – A vintage ribbon loudspeaker that was originally produced in the 1980s and features a curved ribbon diaphragm.
- Eminent Technology LFT-8 – is a high-end loudspeaker system designed for audiophiles and music enthusiasts. It was first introduced in the late 1990s and uses a thin, lightweight diaphragm to produce sound.he LFT-VIII is a hybrid planar magnetic and dynamic driver loudspeaker that features eight 8-inch planar magnetic panels and two 10-inch dynamic woofers. It has a frequency response range of 20 Hz to 23 kHz and a sensitivity rating of 86 dB.
- GoldenEar Technology Triton Reference – A floor-standing loudspeaker that features a folded ribbon tweeter, a high-definition midrange driver, and two 8-inch subwoofers.
Note that this is not an exhaustive list and there are many other ribbon loudspeakers available from various manufacturers.
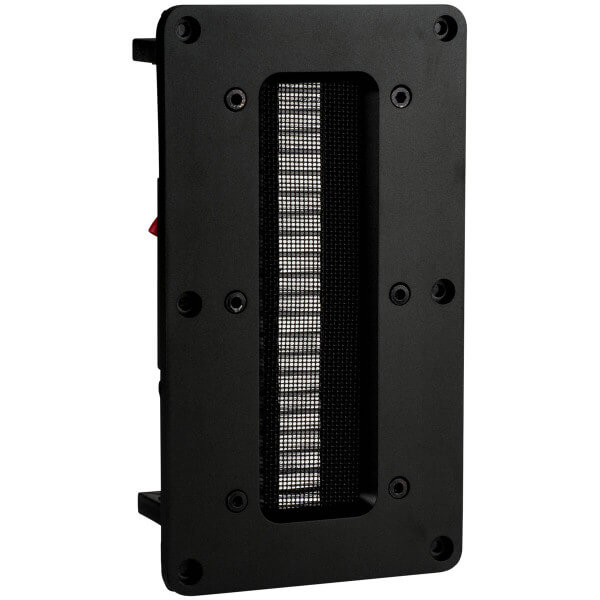









































leon
November 26, 2023 at 1:20 am
Ribbon and FOLDED ribbon are not quite the same.
Folded ribbon, like the Heil AMT has been around for a while. Some consider it fragile. These are not expensive tweeters and everyone from EMOTIVA to Parts Express use them. I don’t think they are dipole or dipole, either.
A True Ribbon, OTOH is a tall driver and radiates out the front and rear…producing a unique sound signiture.
Do not confuse the magnepan name of Quasi Ribbon with a real ribbon. The QR drivers are a variation on the Jim Winey invented ‘planar magnetic’ which originally used wire….not the current ‘flat’ wire which Magnepan insists on calling a ribbon….